In year 10 students have 30 lessons a week, these are allotted as follows:
Number of lessons per subject
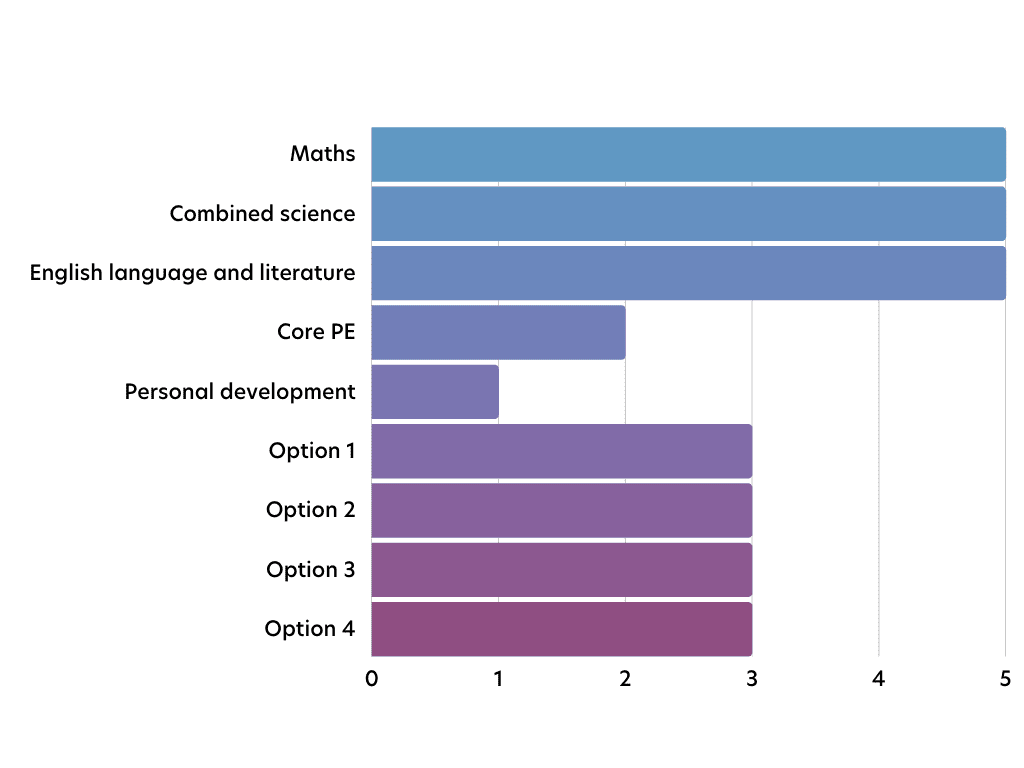
Below is a general overview of the topics students are taught throughout the year in each subject.
Year 10 students on the red pathway study English, maths, science, physical education, personal development, French and either history or geography, they also choose to pursue two further subjects.
Students on the blue pathway study the same core subjects as above with the exception of French, students therefore have three additional subjects to choose.
For a more in depth outline of each subject please click on the link for the subject page.
If you would like to speak to us about any aspect of our curriculum please get in touch.
Core subjects
Students study these core subjects.
Additionally they will choose between history or geography and, depending on their pathway, may have French as a core subject (please see the optional subject list to learn more about these subjects).
English
Autumn term 1
Literature Paper 1 Shakespeare and the 19th Century novel: Shakespeare – Romeo and Juliet
- Read, understand and respond to texts. Maintain a critical style and develop a personal response; use textual references including quotations, to support and illustrate interpretations.
- Analyse the language, form and structure used by a writer to create meanings and effects, using relevant subject terminology.
- Show understanding of the relationships between texts and contexts in which they were written.
- Use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect; with accurate spelling and punctuation.
Autumn term 2
Literature Paper 1 Shakespeare and the 19th Century novel: Charles Dickens – A Christmas Carol
- Read, understand and respond to texts. Maintain a critical style and develop a personal response; use textual references, including quotations, to support and illustrate interpretations.
- Analyse the language, form and structure used by a writer to create meanings and effects, using relevant subject terminology.
- Show understanding of the relationships between texts and the contexts in which they were written.
Spring term 1
Language Paper 1 Explorations in Creative Reading and Writing: Section B – Writing
- Communicate clearly, effectively and imaginatively; selecting and adapting tone, style and register for different forms, purposes and audiences
- Organise information and ideas, using structural and grammatical features to support coherence and cohesion of texts
- Use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate spelling and punctuation
Spring term 2
Poetry: Anthology / Unseen poetry
- Read, understand and respond to texts. Maintain a critical style and develop a personal response; use textual references, including quotations, to support and illustrate interpretations
- Analyse the language, form and structure used by a writer to create meanings and effects, using relevant subject terminology
- Show understanding of the relationships between texts and contexts in which they were written
Spring term 2
Language Paper 1 Explorations in Creative Reading and Writing: Section A – Reading
- Identify and interpret explicit and implicit information and ideas
- Explain, comment on and analyse how writers’ use language and structure to achieve effects and influence readers, using relevant subject terminology to support their views
- Evaluate texts critically and support this with appropriate textual references
Summer term 1
Literature Paper 2 Modern Texts and Poetry: J. B. Priestley – An Inspector Calls
- Read, understand and respond to texts. Maintain a critical style and develop a personal response; use textual references, including quotations, to support and illustrate interpretations
- Analyse the language, form and structure used by a writer to create meanings and effects, using relevant subject terminology
- Show understanding of the relationships between texts and contexts in which they were written
- Use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate spelling and punctuation
Summer term 2
Literature Paper 2 Modern Texts and Poetry: J. B. Priestley – An Inspector Calls
- Read, understand and respond to texts. Maintain a critical style and develop a personal response; use textual references, including quotations, to support and illustrate interpretations
- Analyse the language, form and structure used by a writer to create meanings and effects, using relevant subject terminology
- Show understanding of the relationships between texts and contexts in which they were written
- Use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate spelling and punctuation
Spoken language endorsement
- Be audible
- Use Spoken Standard English
- Be intelligible
- Use language appropriate to the formal setting of the presentation
- Express ideas
- Organised and structured speech
- Meet the needs of the audience
- Listen and respond to questions.
Maths
Autumn term
Geometry and Transformations
- Pythagoras
- Trigonometry
- Transformations
- Congruence and similarity
- Probability
- Tree diagrams
- Frequency trees
- Venn diagrams
Spring term
Number and measures
- Percentages
- Sequences
- Proof
- Area and perimeter
- Volume and surface area
- Sectors
Summer term
Transformations
- Loci recap
- Trigonometry recap
- Iteration
- Circle equations
- Powers/roots
- Surds
Personal development (including RE)
Autumn term
Work experience/law and order
- How to write a CV
- Choosing a work experience placement
- Writing a speculative letter
- Happiness and positivity
- Managing grief and bereavement
- Social anxiety
- Terrorism
- Overt and covert racism
Spring term
Living responsibly/law abiding citizen
- Managing time
- Living sustainably
- Homelessness
- How the criminal justice system works
- Antisocial behaviour
- County lines
- Money laundering
- Hate crime
Summer term
Peace and justice (see RE curriculum)/getting on
- Relationships and role models
- Same sex relationships
- Gender and trans identity
- Parenting
- Work experience preparation
- Health and safety in the work place
- Work experience review
Visit our personal development page for more information
Religious education
- Should Christians forgive?
- How do Christians justify war?
- Do people who do wrong ever get justice?
- Why do we punish people who do wrong?
- Why should Christians stand up for those who are oppressed?
- How influential are Christian values on our prison system?
Physical education
| Girls | Boys |
| Trampolining | Football |
| Table tennis | Rugby |
| Tag rugby | Handball |
| Handball | Boxercise |
| Boxercise | Trampolining |
| Netball | Table tennis |
| Rounders | Rounders |
| Athletics | Athletics |
| Fitness | Fitness |
| Football | Cricket |
| Softball | |
| Frisbee |
Science (combined)
Autumn term
- Cell biology
- Organisation
- Atomic structure and the Periodic Table
- Energy
Spring term
- Infection and response
- Structure and bonding
- Chemical calculations and changes
- Matter and radiation
Summer term
- Bioenergetics
- Electrolysis and energy changes
- Forces in action
Optional subjects
Additionally students choose to study two/three of the subjects listed below.
Art
Autumn term
Fundamental elements and ‘expression’
- Fundamental elements
- Introduction to first topic ‘expression’
- Drawings and 3D responses
Spring term
Beautiful decay
- Drawing
- Painting techniques
- Development skill
- Material exploration
- Final outcomes
- Analysis
Summer term
Mini mock
- Students will be given various starting points to develop a personal response
- Exploring appropriate media, materials, techniques and processes.
Business and enterprise
Unit 1 – introduction to business and enterprise
Autumn term
- Entrepreneurial characteristics and business aims and objectives
- Legal structures, organisational structures and stakeholder engagement
Spring term
The marketing mix, market research, market types and orientation types
Summer term
- Sources of enterprise funding and business finance
- Business and enterprise funding
- Funding types
- Financial terms, documents and tools
- Financial terms and calculations
- Costs, liabilities and assets
- Financial documents
- Ratio analysis
- Cash flow management
- The impact of the external environment on business and enterprise
- The impact of the internal environment
- External influences
Child development and care
Autumn term
- Physical development
- Cognitive development
- Communication and language development
- Social and emotional development
- Nature v nurture
- Biological factors that can affect development
- Environmental factors that can affect development
- Transitions and how they affect development
- Supporting transitions
- Building relationships
- Child centred approach
Spring term
- Child care settings and sectors
- Preparing for placement
- Responsibilities of care workers
- Meeting the individual needs of children
- Diversity and inclusion
- Learning styles
- Study skills
- Coursework 1
Summer term
- Coursework 1 child development 0-5
- Exam preparation
Visit our child development and care page for more information
Computer science
Autumn term
- System architecture
- Memory
- Computational thinking
Spring term
- Data storage
- Characters
- Networks and hardware
Summer term
- Wireless connections
- Network topologies, layers and protocols
- Producing robust programs
Creative i-Media
Autumn term
• Types of digital graphic
• Uses of digital graphics
• File types
• Compression
Spring term
• Mind maps
• Visualisation diagrams
• Mood boards
• Work plans
• Storyboards
Summer term
• Sourcing assets
• Legal and ethical considerations
• Image manipulation
• Photo editing
• Reviewing a media product
Creative textiles
Autumn term
Introduction to key skills
- Manipulating fabric
- Surface design techniques
- Presentation techniques
- Digital pattern creation and design
- Drawing and photographing for textiles
Spring term
Introduction to first topic ‘elements’
- Researching
- Textile techniques (building on key skills and combining techniques)
- Photographing
- Development skill
- Final outcomes
- Analysis
Summer term
Mini mock
- Students will be completing an outcome based on the main project explored this term.
Drama
Autumn term
WW1 devising baseline/practitioner workshops
Spring term
Mock/component 1: exploring the performing arts
Summer term
Component 1: exploring the performing arts
Film studies
Autumn term – introduction to key elements
- Cinematography
- Editing
- Sound
- Mise-en-scene
- Genre
Spring term – NEA screenwriting preparation / planning
- Narrative techniques
- Screenwriting structure
- Screenplay study / comparison
- Horror film openings
Summer term – NEA screenwriting drafting
- Computer-room based lessons
- 800-1000 word horror film opening
- 1 page shooting script
- 750 word evaluative analysis
Food and cookery
Autumn term
- Weighing and measuring
- Chopping techniques
- Peeling/whisking
- Rub-in techniques
- Sensory perception of food
- Cooking/baking techniques
Spring term
- Food legislation and provenance (food crime)
- Bread (practical module)
- Baking (practical module)
- Pastry (practical module)
Summer term
- Investigating storage and presentation of food. Looking at specific techniques used in the industry such as hot holding, portion control and garnish
French
Autumn Term
Theme: identity and culture
Technology in everyday life
- Talk about the uses of social media
- Discuss pros and cons of social media
- Discuss the uses of mobile technology
- Discuss the benefits and dangers of mobile technology
Free time activities
- Describe free time activities in general
- Talk about your free times in the past
- Talk about sports you do and discuss extreme sports
- Talk about food and drink (world food and eating habits)
Spring Term
Theme: identity and culture, local, national, international and global areas of interest
Customs and festivals
- Talk about how you celebrate festivals
- Discuss what tradition means to you
- Describe international festivals
- Describe an event (celebration) in detail (past/present and future)
Home, town, neighbourhood and region
- Describe your home
- Describe your ideal home
- Talk about your town – what it’s like and what there is to do
- Describe your region
Summer Term
Theme: local, national, international and global areas of interest
Charity and voluntary work
- Describing charity work
- Understanding the importance of charities
- Heathy eating – comparing old and new
- Describing health resolutions
Environment and poverty
- Discuss environmental problems and actions
- Discuss social issues
- Discuss inequalities
Geography
Autumn term
• Living world; deserts and rainforest
• Urban world; Birmingham and Rio de Janeiro
Spring term
• Rivers
• Managing resources
Summer term
• Fieldwork – Birmingham and Peak District
Graphic communication
Autumn term
- Introduction to graphic communication
- Typography
- Key terminology
- Influential designers from around the world
- Illustration
Spring term
Client brief response – key elements to be explored
- Colour
- Composition
- Shape
- Pattern
- Scale
- Stylisation
- Digital drawing
- Typography
- Illustration
Summer term
Introduction to sustained phase
Students will be given three suggested starting points:
-
- Food wastage
- Charity campaigns
- Teenage health issues
- Book design
- Greetings cards
- CD, vinyl or album covers
- Shop graphics
- Packaging for a range of mobile phones
Mini mock
-
- Students will be given various starting points to develop a personal response.
- Exploring appropriate media, materials, techniques and processes.
History
Autumn term and half term 1 of the Spring term
Medicine through time [thematic study] – looking at beliefs in causes, treatments, prevention and medical care.
- Medieval medicine
- Renaissance medicine
- The Industrial Age
- The Modern Age
- The British sector of the Western Front – WW1 and the impact on medicine – a case study looking at how the demands of war and conditions in the trenches lead to developments in medicine.
Half term 2 of the spring term and half term 1 of the summer term
Anglo-Saxon and Norman England [British depth study] – examines Anglo-Saxon England focusing on how society was structured and how government operated. The unit then moves to look at the impact of the Norman invasion and the social, political, cultural and economic changes that resulted.
- Anglo-Saxon England and the Norman Conquest
- How William I secured England
- Norman England
Half term 2 of the summer term
American West [period study] – Students look at how the United States of America was formed between 1835-1895. Thinking in particular about migration and settlement, removal and destruction of the Native American people, and development of transportation and industry.
- Early settlement of the Plains
- Development of the Plains
- Conflict and conquest
Media studies
Autumn term
- Component 1 set texts section A
- Media language
- Media representation
Spring term
- Component 1 set texts section B
- Media industries
- Media audiences
Summer term
- Component 2 set topics
- Television
- Component 3 creating media products
Music
Autumn term
BTEC unit 2 –Managing a music product
GCSE- Music theory basics and compositional developments
Spring term
If a student decides to continue studying music at key stage 4, we offer two options – GCSE and BTEC. This enables us to cater to students’ different learning styles and interests in music.
BTEC unit 2- managing a music product continued
BTEC unit 4-introdudtion to composition
GCSE- Purcell analysis developments, Beethoven Analysis Developments and composition 1 completion
Summer term
BTEC unit 4 Introduction to composition
BTEC unit 1-The Music Industry Exam
GCSE- Purcell Analysis, Queen analysis
Performance development
PE BTEC
Autumn/spring term
Component 1: preparing participants to take part in sport and physical activity
- Increasing participation in regular sport or physical activity for different types of sports participants.
- Examine equipment and technology required for participants to use when taking part in sport and physical activity.
- Preparing participants to take part in sport and physical activity.
Controlled assessment: March/April
Summer term
Component 2: taking part and improving other participants’ sporting performance
- Understand how different components of fitness are used in different physical activities.
- Participate in sport and understand the roles and responsibilities of the officials.
- Demonstrate ways to improve participants’ sporting techniques.
Photography
Autumn term
Skills
- Aperture
- Force Perspective
- Angles
- Framing
- Rule of thirds
- Editing – spot colour, contrast, filters.
- Multiplicity
- Blending
- Slow shutter speed
- Fast shutter speed
Spring term
Colour photography/ independent topic
Students will start their first independent topic based on ‘Colour’. This will enable them to develop an understanding of how a coursework project is put together and build upon the skills learnt in term one with a bit more freedom to experiment. This will run during the first half of the term, the second half students will receive a series of starting points to develop out.
- Researching photographers
- Analysis of work
- Planning of photo-shoots
- Independent development of ideas
- Photo-shoot exploration and creativity.
- Editing experimentation.
Summer term
Mini mock
- Students will be given various starting points to develop a personal response
- Exploring appropriate media, materials, techniques and processes.
Product design
Autumn term
- Introduction to the course
- Key skills and elements needed in the industry
- Technical drawing introduction
- Wood
- Tool box project
- Candle stick project
Spring term
- Speaker project
- Functionality
- Aesthetics
- Environmental factors
- Availability
- Cost
Summer term
- Chair project
Religion, ethics and philosophy
The course will cover core fundamental beliefs of Islam and Christianity, specifically applying them to moral issues such as abortion, euthanasia, reasons for war, terrorism, crime and punishment and many more.
Visit our religion, ethics and philosophy page for more information
Science (separate)
Autumn term
- Biology: cell biology
- Chemistry: atomic structure and the Periodic Table; structure and bonding
- Physics: energy
Spring term
- Biology: infection and response
- Chemistry: chemical calculations and changes
- Physics: electricity
Summer term
- Biology: bioenergetics; organisation
- Chemistry: electrolysis and energy changes
- Physics: matter and radiation; forces in balance and pressure
Statistics
Autumn term
Collection of data
- Types of data
- Sampling
- Collecting data
Spring term
Processing and representing data
- Tables/charts and diagrams
- Distributions of data
Summer term
Time series
- Times series
- Moving averages
- Trends
Probability
- Experimental probability
- Probability diagrams
- Mutually exclusive and exhaustive events
- Independent events
- Probability distributions
CoPE (ASDAN pathway)
- Health and fitness
- Independent living
- Sport and leisure
- Communication
- Beliefs and values
- International issues
- Citizenship and community




