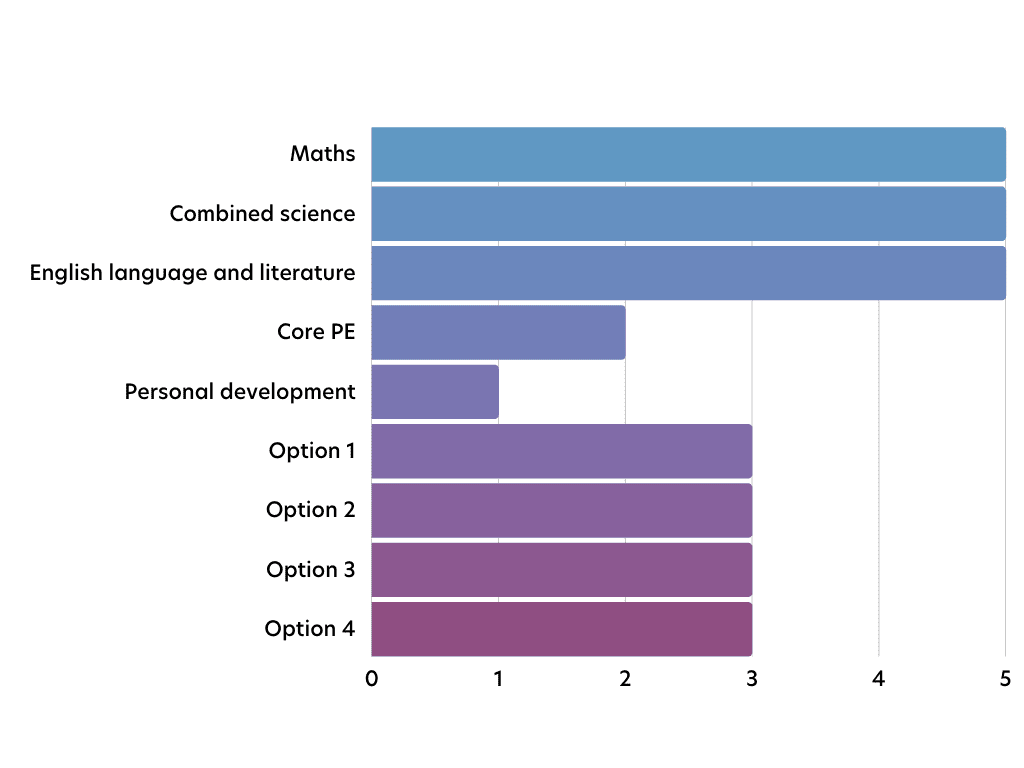
In year 11 students have 30 lessons a week, these are allotted as follows:
Number of lessons per subject
Below is a general overview of the topics students are taught throughout the year in each subject.
Year 11 students on the red pathway study English, maths, science, physical education, personal development, French and either history or geography, they also choose to pursue two further subjects.
Students on the blue pathway study the same core subjects as above with the exception of French, students therefore have three additional subjects to choose.
For a more in depth outline of each subject please click on the link for the subject page.
If you would like to speak to us about any aspect of our curriculum please get in touch.
Core subjects
Students study these core subjects.
Additionally they will choose between history or geography and, depending on their pathway, may have French as a core subject (please see the optional subject list to learn more about these subjects).
English
Autumn term 1
Literature Paper 2 Modern Texts and Poetry: Anthology / Unseen poetry
- Read, understand and respond to texts. Maintain a critical style and develop a personal response; use textual references, including quotations, to support and illustrate interpretations
- Analyse the language, form and structure used by a writer to create meanings and effects, using relevant subject terminology
- Show understanding of the relationships between texts and contexts in which they were written
Language Paper 2 Writers’ viewpoints and perspectives: Section A – Reading
- Identify and interpret explicit and implicit information and ideas
- Explain, comment on and analyse how writers use language and structure to achieve effects and influence readers, using relevant subject terminology to support their views
- Compare writers’ ideas and perspectives, as well as how these are conveyed, across two or more texts
Autumn term 2
Literature Paper 2 Modern Texts and Poetry: Anthology / Unseen poetry
- Read, understand and respond to texts. Maintain a critical style and develop a personal response; use textual references, including quotations, to support and illustrate interpretations
- Analyse the language, form and structure used by a writer to create meanings and effects, using relevant subject terminology
- Show understanding of the relationships between texts and contexts in which they were written
Language Paper 2 Writers’ viewpoints and perspectives: Section B – Writing
- Communicate clearly, effectively and imaginatively; selecting and adapting tone, style and register for different forms, purposes and audiences
- Organise information and ideas, using structural and grammatical features to support coherence and cohesion of texts
- Use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect; with accurate spelling and punctuation
Revision – Literature Paper 2 Modern Texts and Poetry: J. B. Priestley – An Inspector Calls
Spring term 1
- Revision – Literature Paper 1 Shakespeare and the 19th Century novel
- Revision – Language Paper 1 Explorations in Creative Reading and Writing
Spring term 2
- Revision – Literature Paper 2 Modern Texts and Poetry
- Revision – Language Paper 2 Writers’ viewpoints and perspectives
Summer term 1
Revision for the summer exams
Maths
Autumn term
Graphs and algebra
- Gradients and lines
- Non-linear graphs
- Using graphs
- Expanding and factorising
- Changing the subject
- Functions
Spring term
Reasoning and revision
- Multiplicative reasoning
- Geometric reasoning
- Algebraic reasoning
- Transforming and constructing
- Revision
Personal development (including RE)
Autumn term
Careers and post 16 transition
- Presenting personal information
- Writing a personal statement
- How to apply
- Application forms
- Mock interview applications
- How to ace an interview
- Review interview skills and target set
Spring term
GCSE revision skills and managing stress
- Study skills
- Revision techniques
- Trade unions
- Sexual harassment
- Marriage
- Self-examination and screening
- Issue-based topics chosen by the class
Visit our personal development page for more information
Religious education
- Sanctity of human life
- Death penalty
- Medical interventions
- Forced and arranged marriages
- Right wing extremism
- Community cohesions
- Terrorism and holy war
- Suicide
- IVF
- Cloning
- Euthanasia
Physical education
| Girls | Boys |
| Trampolining | Football |
| Table tennis | Rugby |
| Tag rugby | Handball |
| Handball | Boxercise |
| Boxercise | Trampolining |
| Netball | Table tennis |
| Rounders | Rounders |
| Athletics | Athletics |
| Fitness | Fitness |
| Football | Cricket |
| Softball | |
| Frisbee |
Science (combined)
Autumn term
- Homeostasis and response
- Inheritance, variation and evolution
- Rates of reaction, equilibrium and organic chemistry
- Waves
Spring term
- Ecology
- Chemical analysis
- The Earth
- Electromagnetism
Optional subjects
Additionally students choose to study two/three of the subjects listed below.
Art
Autumn term
Final project (independent)
- Selecting appropriate starting points
- Selecting appropriate artist/source materials
- Developing initial ideas
- Presentation skills
- Experimentation
- Recording skills
Spring term
Component 2 (NEA) controlled assessment
- Student will be given the starting points as selected by the exam board.
- Students will begin the preparation process which will involve the following:
- selecting appropriate starting point
- developing initial ideas through written and visual presentation
- artist research and source selection
- visual analysis of both primary and secondary research
- material experimentation
- ideas refinement
- record refinements
- Final idea plan for 10 hour assessment
Business and enterprise
Unit 2 understanding resources for business and enterprise planning
Autumn term
- Research, resource planning and growth for business
- Human resource requirements for a business start-up
Spring term
- Sources of enterprise funding and business finance
- Business and enterprise planning.
Child development and care
Autumn, spring and summer terms
Coursework 2 – working in child care setting
Visit our child development and care page for more information
Computer science
Autumn term
- System security
- Further programming techniques
- Computational logic
Spring term
- System software
- Translators and facilities of language
- Legalities associated with technology
Summer term
- Ethical, cultural and environmental issues linked to technology
- Data representation
Creative i-Media
Autumn term
• Types of digital animation
• Uses of digital animation
• Animation file types
• Analysing a brief
Spring term
• Storyboarding an animation
• Using animation software
• Evaluating an animation
• Types and uses of digital video
• Designing a digital video
Summer term
• Shooting a video
• Editing and cutting
• Evaluating a digital video project
Creative textiles
Autumn term
Final project (independent)
- Selecting appropriate starting points
- Selecting appropriate artist/source materials
- Developing initial ideas
- Presentation skills
- Experimentation
- Recording skills
Spring term
Component 2 (NEA) controlled assessment
- Students will be given the starting points as selected by the exam board
- Students will begin the preparation process which will involve the following:
– selecting appropriate starting point
– developing initial ideas through written and visual presentation
– artist research and source selection
– visual analysis of both primary and secondary research
– material experimentation
– ideas refinement
– record refinements - Final idea plan for 10-hour assessment
Drama
Autumn term
Component 2: Developing skills and techniques in the performing arts
Spring term
Component 3: Responding to a brief
Film studies
Autumn term
Paper 2 section A – Let The Right One In and paper 2 section B An Education
- Representation study
- Narrative study
- Key scenes analysis
- Exam questions
Spring term
Paper 2 section C – Submarine and paper 1 section A, Singin’ in the Rain
- Aesthetics study
- Context study
- Key scenes analysis
- Exam questions
Summer term
Paper 2 section B Grease and paper 2 section C Whiplash
- Critical analysis excerpts
- Context study
- Key scenes analysis
- Exam questions
Food and cookery
Autumn term
- Investigating specific nutrients and their importance in different age groups including people with medical conditions
- Investigating how different cooking methods will affect the nutritional value of certain foods
- What characteristics people show if they are deficient in certain nutrients
- Careers focus in the industry – menu planning for a customer base
Preparation for food presentation
Spring term
- Completion of food presentation involving taste testing
- Revision for written exam
Summer term
Exam preparation and revision
French
Autumn Term
Theme: local, national, international and global areas of interest and current and future study and employment
Holidays and travel
- Describe holiday destinations
- Talk about favourite holidays and activities
- Talk about different places in French (cultural capital)
- Discuss the importance of holidays
Life at school and college
- Describe holiday destinations
- Describe a day at school
- Compare school life in France and Britain
- Talk about school rules and uniform
Mock exam preparation
Spring Term
Theme: current and future study and employment
- Talk about future studies
- Talk about future options
- Talk about jobs and part-time work
- Discussing how to get a job
Summer Term
Exam preparation for listening, reading, writing with a focus on speaking
Geography
- Autumn term
• Coasts
• Economic world – UK and Nigeria - Spring term
• Food
• Hazards
• Decision making
Graphic communication
Autumn term
- Continue with sustained phase
- Preparation for exam
Spring term
- Preparation for controlled assessment
- Seven starting points are provided on the paper and the student selects and responds to one of these
History
Half term 1 of the Autumn term
American West [period study] – students look at how the United States of America was formed between 1835-1895. Thinking in particular about migration and settlement, removal and destruction of the Native American people, and development of transportation and industry. Anglo-Saxon and Norman England combined with American West completes paper 2.
• Early settlement of the Plains
• Development of the Plains
• Conflict and conquest
Half term 2 of the autumn term and spring term
Weimar and Nazi Germany [modern depth study] – starts with the armistice agreement and the setting up of the Weimar Republic through to the rise of Adolf Hitler to the creation of the Nazi state. This completes paper 3.
• The Weimar Republic
• Hitler’s rise to power
• Nazi control and dictatorship
• Life in Nazi Germany
Music
Autumn term
BTEC unit 2 –Managing a music product
GCSE- Music theory basics and compositional developments
Spring term
BTEC unit 5 – composition continued
BTEC unit 4 – performance
GCSE- Purcell analysis developments, Beethoven Analysis Developments and composition 1 completion
Summer term
BTEC unit 4 Introduction to composition
BTEC unit 1-The Music Industry Exam
GCSE- Purcell Analysis, Queen analysis
Performance development
PE BTEC
Autumn term
Component 2: taking part and improving other participants sporting performance
- Understand how different components of fitness are used in different physical activities.
- Participate in sport and understand the roles and responsibilities of the officials.
- Demonstrate ways to improve participants’ sporting techniques.
Controlled assessment: October/November
Spring/summer term
Component 3: developing fitness to improve other participants’ performance in sport and physical activity
- Explore the importance of fitness for sports performance.
- Investigate fitness testing to determine fitness levels.
- Investigate different fitness training methods.
- Investigate fitness programming to improve fitness and sports performance.
Exam: summer term
Photography
Autumn term
Students select their 2 – 3 chosen coursework topics and spend this term improving, refining and developing these topics.
The topic titles are independently chosen and driven by the students, with specialist support from staff to guide and facilitate their ideas.
This is worth 60% of their grade.
Spring term
Students receive their exam paper. This consists of 7 topics set by the exam board. Students select a topic and begin exploring and personalising the outcomes of the topic.
The work leading up to the exam is known as prep work. The exam project is completed during a 10-hour controlled assessment under exam conditions. Students continue to explore and finalise their topic resulting in one or more creative and personal outcomes.
Summer term
Students spend the remaining time on the course consolidating their coursework ready for hand-in at the end of May.
Product design
Autumn term
- Preparation for NEA
- Outcomes for assessment of NEA
Spring term
- Revision for written exam
Summer term
Completion of course work and exam preparation.
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/examspecs/zby2bdm
Religion, ethics and philosophy
The course will cover core fundamental beliefs of Islam and Christianity, specifically applying them to moral issues such as abortion, euthanasia, reasons for war, terrorism, crime and punishment and many more.
Visit our religion, ethics and philosophy page for more information
Science (separate)
Autumn term
- Biology: homeostasis and response
- Chemistry: rates of reaction, equilibrium and organic chemistry; organic reactions and polymers
- Physics: waves
Spring term
- Biology: inheritance, variation and evolution
- Chemistry: chemical analysis
- Physics: forces and motion; electromagnetism
Summer term
- Biology: ecology
- Chemistry: the Earth
- Physics: space
Statistics
Autumn term
Scatter diagrams and correlation:
- Scatter diagrams
- Relationships between data
- Spearman’s rank coefficient
- Pearson’s product moment correlation
Spring term
- Time series
- Moving averages
- Trends
Summer term
Probability
- Experimental probability
- Probability diagrams
- Mutually exclusive and exhaustive events
- Independent events
- Probability distributions





